Key Takeaways
1. CMMC 2.0 builds on the lessons learned from cyber threats like the SolarWinds attack, aiming to bolster DIB cybersecurity and protect sensitive data.
2. Compared to CMMC 1.0, CMMC 2.0 streamlines the framework into three levels of cybersecurity maturity, aligned with National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) standards for clarity and consistency.
3. Implementation of CMMC 2.0 can be made simple with the help of AWA. The AWA experts will help you prepare for security compliance and CMMC assessments in no time.
Overview Of The CMMC Program
The CMMC Framework serves as a standardized guideline within the DoD to ensure consistent implementation of cybersecurity measures across its supply chain.
The DoD aims to guarantee that its contractors and subcontractors can effectively safeguard DoD’s Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and Federal Contract Information (FCI) within their systems.
Moreover, this program offers the DoD greater confidence that its partners follow cybersecurity standards for programs and systems handling sensitive information.
What Was CMMC 1.0?
CMMC 1.0 introduced a tiered approach with five distinct levels (Levels 1-5) to categorize defense contractors based on their cybersecurity readiness.
Each level corresponded to specific requirements that contractors needed to fulfill, determined by the level assigned to their defense contract by the contracting officer.
In addition to setting these compliance standards, CMMC 1.0 proposed the implementation of third-party cybersecurity audits to ensure companies met the regulation’s requirements.
To date, the CMMC 1.0 framework is obsolete and no longer promoted or used.
What is CMMC 2.0?
CMMC 2.0 represents the CMMC program’s evolution, refining its cybersecurity approach. This version simplifies the framework by consolidating requirements into three distinct levels of cybersecurity maturity while it was five levels before.
Moreover, it aligns the criteria at each level with established and widely recognized cybersecurity standards set by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
This strategic alignment with NIST standards enhances clarity and consistency in meeting cybersecurity requirements across organizations.
Note: The assessment in CMMC 2.0 lasts for 3 years and needs to be renewed every three years to stay up to date.
CMMC 1.0 vs CMMC 2.0: What Are The Differences?
CMMC 2.0 brings some notable differences compared to CMMC 1.0. One significant change is the increase in the number of security domains. These new domains cover aspects more relevant to daily operations, like Incident Response, Anomaly Detection, Supply Chain Risk Management, and System Security Planning.
Now, let’s dive into the main differences between the certifications you need to be aware of:
Certification Levels
In CMMC 1.0, there were five certification levels, whereas CMMC 2.0 has condensed them to three. These levels are crucial for determining the security requirements of each contract.

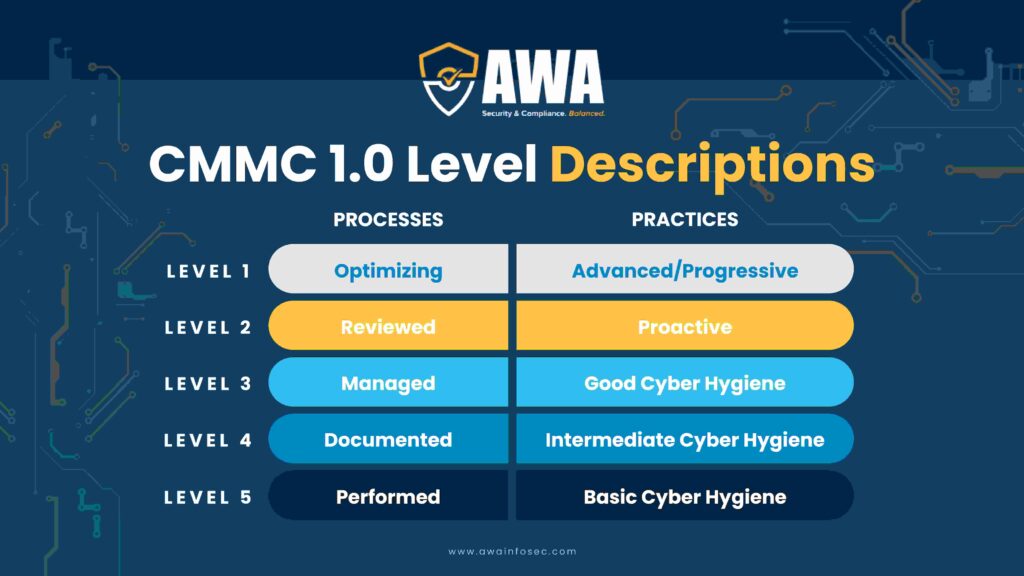
CMMC 1.0 Certification Levels
CMMC Level 1
Known as Basic Cyber Hygiene in CMMC 1.0, it focused on fundamental cybersecurity practices necessary to safeguard federal contract information. This level required organizations to adhere to 17 specified practices, akin to those outlined in 48 CFR 52.204-21 for protecting contractor information systems handling FCI.
CMMC Level 2
Known Intermediate Cyber Hygiene represented a step up, including a selection of requirements from NIST SP 800-171 and other standards. Certification at this level shows that a company has established and documented essential policies and practices.
CMMC Level 3
Termed Good Cyber Hygiene, it targeted the protection of CUI. This level included all security requirements from NIST SP 800-171, supplemented by an additional 20 practices. Organizations seeking Level 3 certification were required to maintain a plan demonstrating compliance with CMMC.
CMMC Level 4
Known as Proactive Cyber Hygiene, it represented a higher level of cybersecurity readiness. Organizations eligible for Level 4 certification had to demonstrate the capability to assess and enhance practices for effectiveness, specifically in safeguarding CUI from advanced persistent threats (APTs).
CMMC Level 5
Referred to as Advanced Cyber Hygiene, it set the bar for the most rigorous cybersecurity standards. At this level, organizations were expected to standardize and optimize processes across their operations, prioritizing the protection of CUI from APTs. Achieving Level 5 certification required managing a total of 171 practices.
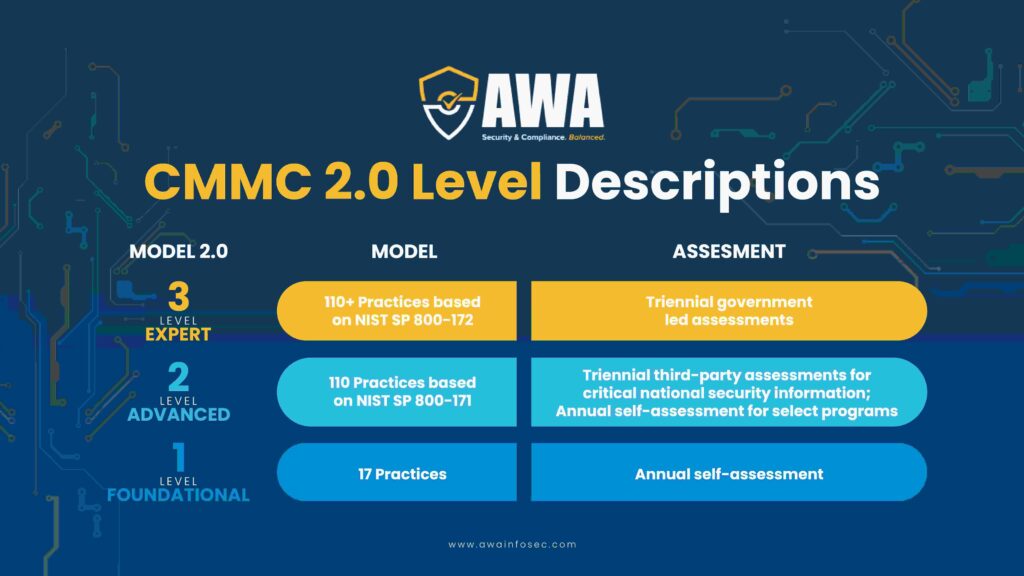
CMMC 2.0 Certification Levels
Level 1 (Foundational Level)
CMMC 2.0’s Level 1, known as the ‘foundational’ level, applies specifically to organizations handling FCI. Similar to Level 1 in CMMC 1.0, its primary focus is safeguarding FCI and controlling access to confidential data for authorized users. With 17 controls, Level 1 aligns closely with the requirements outlined in FAR 52.204-21.
Level 2 (Advanced Level)
Moving up to Level 2 in CMMC 2.0, referred to as the ‘advanced’ level, it targets organizations dealing with CUI. Similar to Level 3 in CMMC 1.0, Level 2 requirements draw from NIST SP 800-171, streamlining processes by eliminating unique maturity practices. Instead, it focuses on aligning with 14 control families and 110 security controls established by the NIST to enhance data security.
Level 3 (Expert Level)
At the pinnacle of CMMC 2.0 is Level 3, known as the ‘expert’ level. Designed to mitigate risks from APTs, it’s geared towards organizations handling high-priority CUI. Similar to Level 5 in CMMC 1.0, Level 3’s security requirements are still being defined by the DoD. However, it’s anticipated that they will be based on the 110 controls from NIST SP 800-171 and a subset of controls from NIST SP 800-172.
Domain Structure
In CMMC 1.0, there were 17 cybersecurity domains, each representing a distinct set of security practices (controls) with similar attributes. However, in CMMC 2.0, the framework comprises 14 cybersecurity domains, three fewer than in CMMC 1.0.
Each domain includes a group of security practices that share common characteristics and are essential for safeguarding FCI and CUI, whether independently or in combination.
The table below provides an overview of the domains outlined in the CMMC framework for protecting FCI and CUI:
| CMMC 1.0 Domains | CMMC 2.0 Domains |
| 1. Access Control | 1. Access Control |
| 2. Asset Management | 2. Awareness and Training |
| 3. Audit and Accountability | 3. Audit and Accountability |
| 4. Awareness and Training | 4. Configuration Management |
| 5. Configuration Management | 5. Identification and Authentication |
| 6. Identification and Authentication | 6. Incident Response |
| 7. Incident Response | 7. Maintenance |
| 8. Maintenance | 8. Media Protection |
| 9. Media Protection | 9. Personnel Security |
| 10. Personnel Security | 10. Physical Protection |
| 11. Physical Protection | 11. Risk Assessment |
| 12. Recovery Planning | 12. Security Assessment |
| 13. Risk Management | 13. System and Communications Protection |
| 14. Security Assessment | 14. System and Information Integrity |
| 15. Situational Awareness | |
| 16. System and Communications Protection | |
| 17. System and Information Integrity |
Third-party Assessors
Under the CMMC 2.0 model, the involvement of Certified Third-Party Assessment Organizations (C3PAOs) is mandated for organizations seeking certification at Level 2 and Level 3. These C3PAOs play a crucial role in the DIB supply chain by assessing and certifying companies’ compliance with the cybersecurity requirements outlined in the CMMC standard.
C3PAOs are responsible for conducting detailed evaluations to confirm compliance with the CMMC standard and issuing certificates to qualifying organizations. Also, they act as trusted entities tasked with ensuring that companies in the DIB supply chain uphold strong cybersecurity measures aligned with the CMMC framework.
Level of independent assessment
In the latest version of CMMC 2.0, Level 1 and some Level 2 contractors can do their own assessments. However, Level 2 contractors should only expect to undergo an independent assessment once the DoD sets rules for annual self-assessment.
Need of annual confirmation
Each year, CMMC 2.0 mandates an annual confirmation from a senior company representative. Here, the Department of Justice (DOJ) intends to hold accountable any entities who knowingly misrepresent their cybersecurity practices.
Companies must assess their procedures for completing this confirmation, decide who will sign it, and establish the criteria needed to feel confident signing it.
POA&Ms and waivers in CMMC 2.0 are limited
Under this change, only a few waivers will be granted. Waivers in CMMC 2.0 allow certain mission-critical needs to skip specific CMMC requirements. This only benefits a select group of contractors.
Plan of Action and Milestones (POA&Ms) will only be needed for minor requirements after your organization achieves higher compliance levels. A POA&M document lists tasks, resources, and deadlines to achieve certain goals. In CMMC 2.0, POA&Ms are permitted in specific situations to assist companies in getting certified.
Why Did the DoD Roll Out the CMMC Program?
The DoD introduced the CMMC program in response to the escalating threat of cyberattacks, which pose a significant risk to the nation’s economic and national security. With high-profile cyber incidents making headlines, it’s evident that the frequency and sophistication of these attacks are on the rise.
Initially, the DoD relied on contractors’ self-attestation, but in September 2020, they introduced CMMC 1.0. However, contractors found it overly complex and inflexible, leading to the abandonment of the program.
In November 2021, the DoD announced CMMC 2.0 to address industry concerns and align program goals with contractor cybersecurity risk management. Now, CMMC 2.0 has reached the proposed rule stage, signaling the government’s commitment to improving cybersecurity practices among defense contractors.
Advantages of CMMC 2.0 For Organizations
Here are some of the advantages of getting CMMC 2.0 certified:
Security
This is a no-brainer! Being CMMC qualified raises the bar for your company’s security standards by manifold. Moreover, the best practices aligned with CMMC help you reduce the chances of getting breached or any other espionage attack from bad actors.
Improves your customer trust
With all the big data breaches happening, businesses are extra cautious about the cybersecurity measures of the companies they work with. Hence, when you are CMMC compliant, you show that you take proper measures to safeguard sensitive data seriously.
This clear and recognized standard assures even the most discerning clients and partners that their information is in safe hands.
Fulfill your contractual obligation to safeguard CUI
CMMC was created to safeguard CUI and FCI. This is why it exists. Hence, if you’re handling CUI in any way, it’s your contractual obligation to protect it from cyber threats. And being CMMC certified helps with just that!
Become more competitive in the market
Having top-notch cybersecurity makes you more competitive. Nowadays, supply chain security is essential, not just a bonus. If a business doesn’t focus on security, it could lose important contracts and partnerships.
When Will CMMC 2.0 Be Required?
A phased rollout of CMMC 2.0 was started in May 2023, with the entire process slated for completion by October 2025. As we approach 2024, some DoD contractors have already requested that their subcontractors comply with the upcoming requirements.
This allows subcontractors to prepare early and ensure they meet the necessary standards before the official implementation date.
Overall, CMMC 1.0 paved the way for cybersecurity improvements, but CMMC 2.0 addresses its shortcomings. With a refined framework, CMMC 2.0 is now more efficient and effective, benefiting all stakeholders.
This improvement definitely strengthens cybersecurity, helping your organization protect sensitive data and ensure secure information systems across the DIB.
How can AWA help you get CMMC certified?
As a C3PAO candidate, AWA is well-equipped to assist organizations in meeting CMMC requirements and preparing for security compliance assessments.
Whether you need assessments or help setting up security measures, AWA has personalized solutions for you. Get expert solutions from AWA and allow our seasoned auditors to help you comply with the new CMMC requirements.
Talk to us today to get the proper assistance in achieving CMMC compliance.





